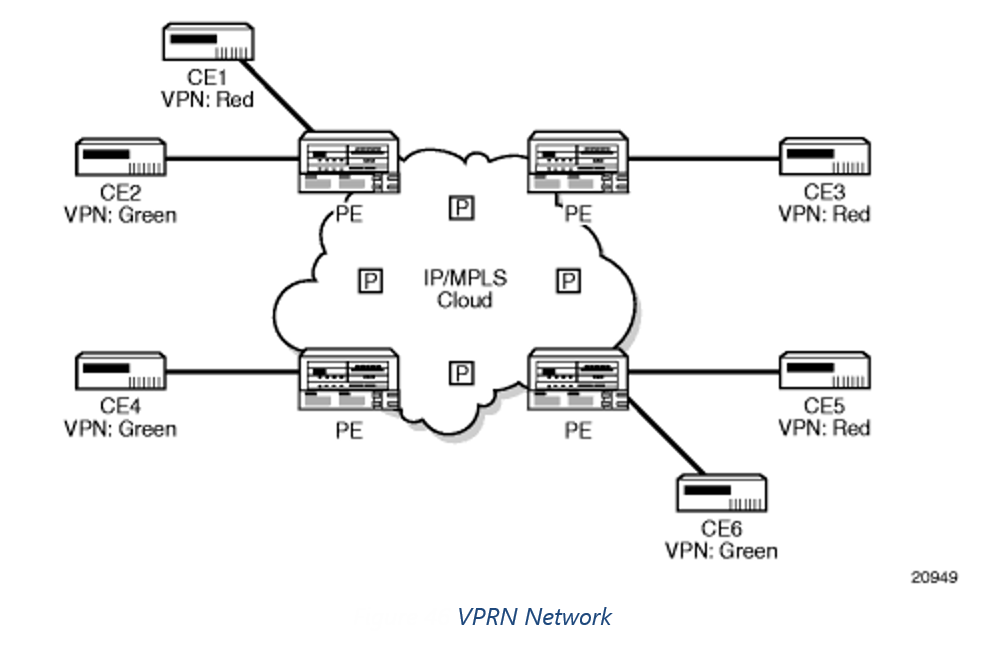
VPRN VPN
VPRN is presented with the same structure in Nokia/Alcatel SAM as VPLS in that multiple VPRN with the same Service IS are represented under one VPRN container. In the case of VPRN however instead of L2 Access Ports VPRN has L3 Access Ports which have an IP Address.
Note that similar to VPLS VPRN can exist within a single router/switch with no service tunnel.
SAM Modelling
Nokia/Alcatel SAM Models VPLS with the following hierarchy:
VPLS -> SITES -> L3 Interfaces -> Service Tunnel
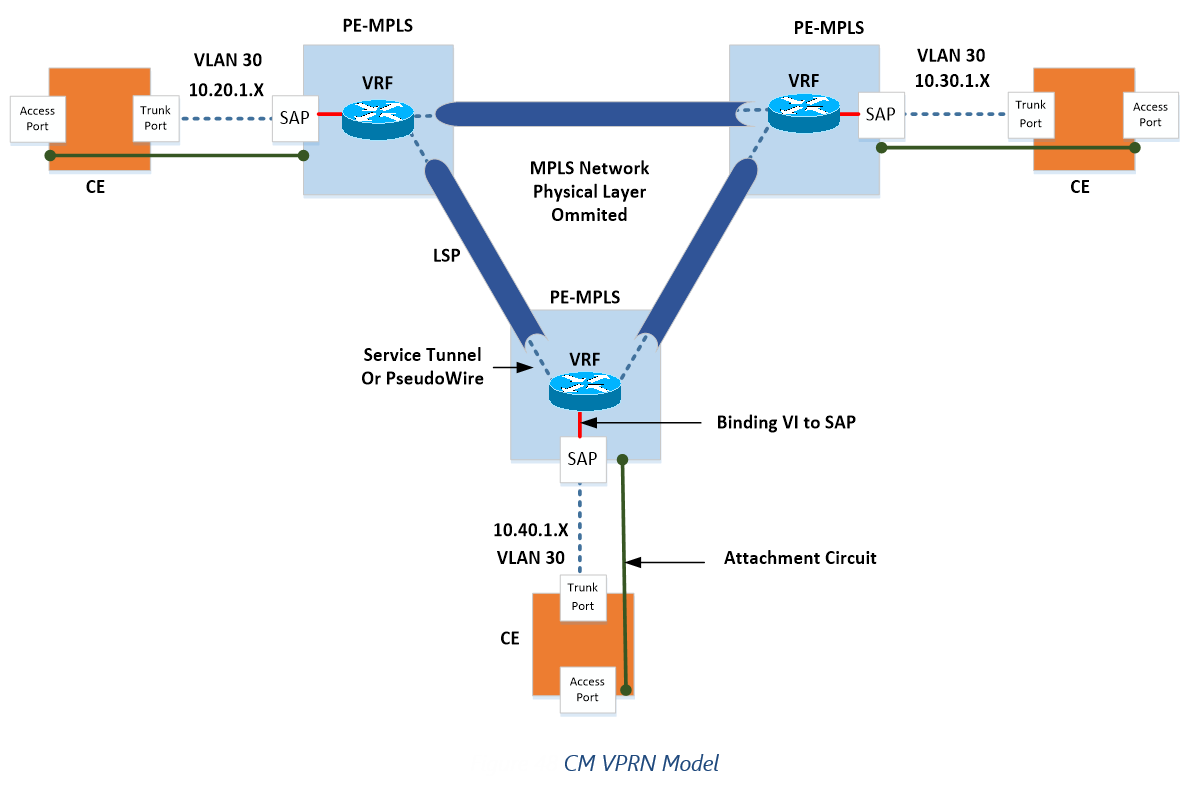
ConnectMaster Modelling
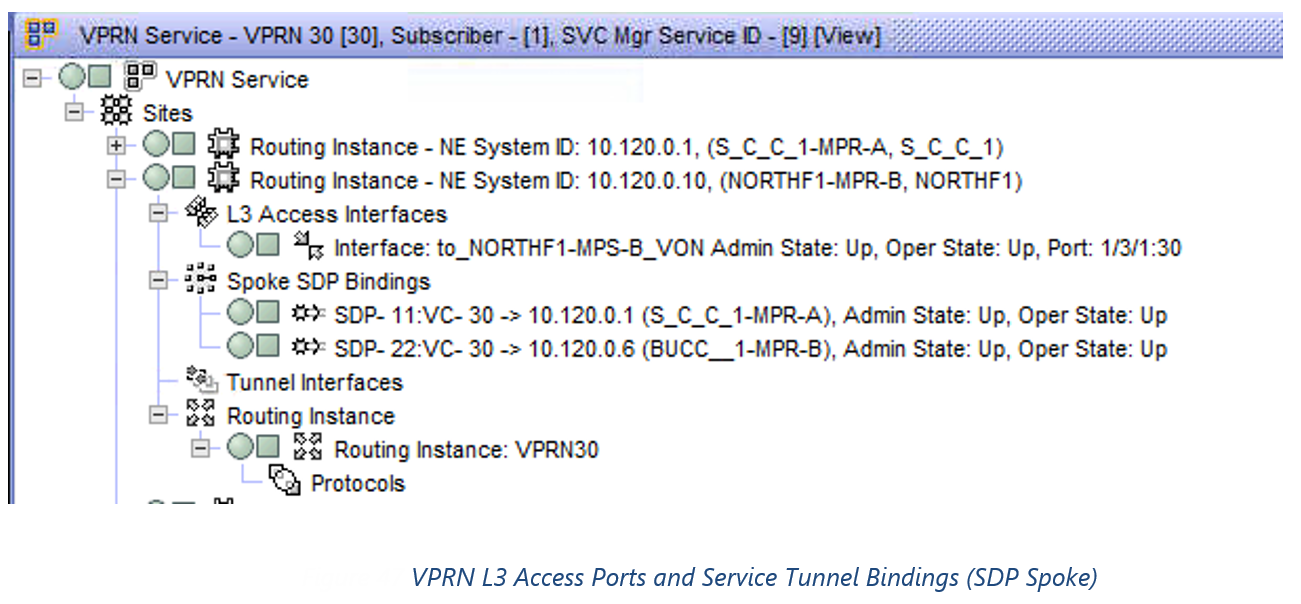
In ConnectMaster the VPRN will be modelled as VPRN with the following characteristics:
1)Service Tunnel Bindings
2)n x SAP Ports (IP Address stored in FA_IPAddress) created under a VRF (Virtual Instance)
Whilst technically IP Addresses can be added directory to a VRF to support functions like VRRP. The only VRRP services seem to be IES which can be configured manually.
Note: IP Address of the VRF does not have to specifically tagged against the SAP, as it was already associated with the virtual sub-port when it was created. See Logical Ports and VLANs Section 0
.
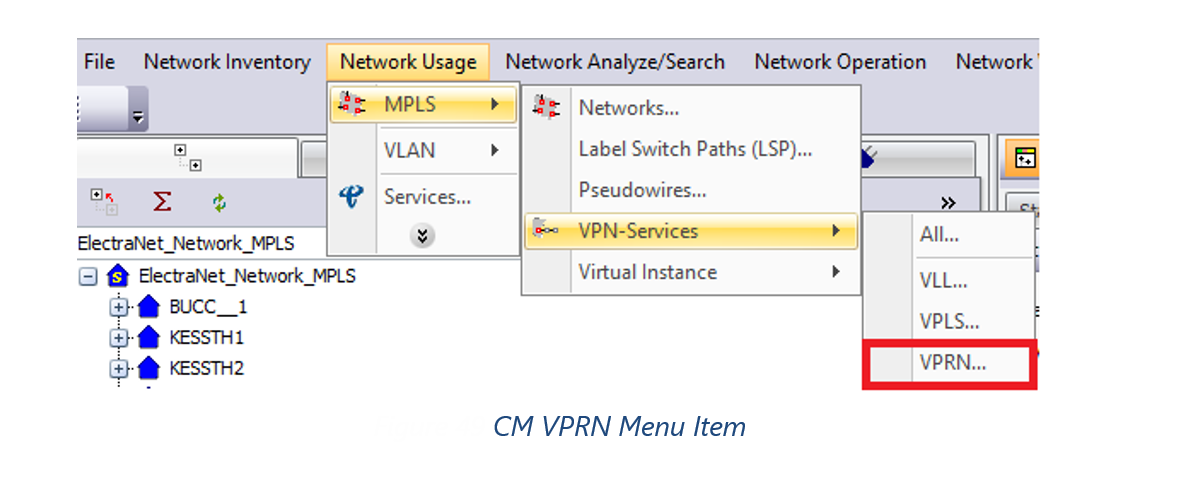
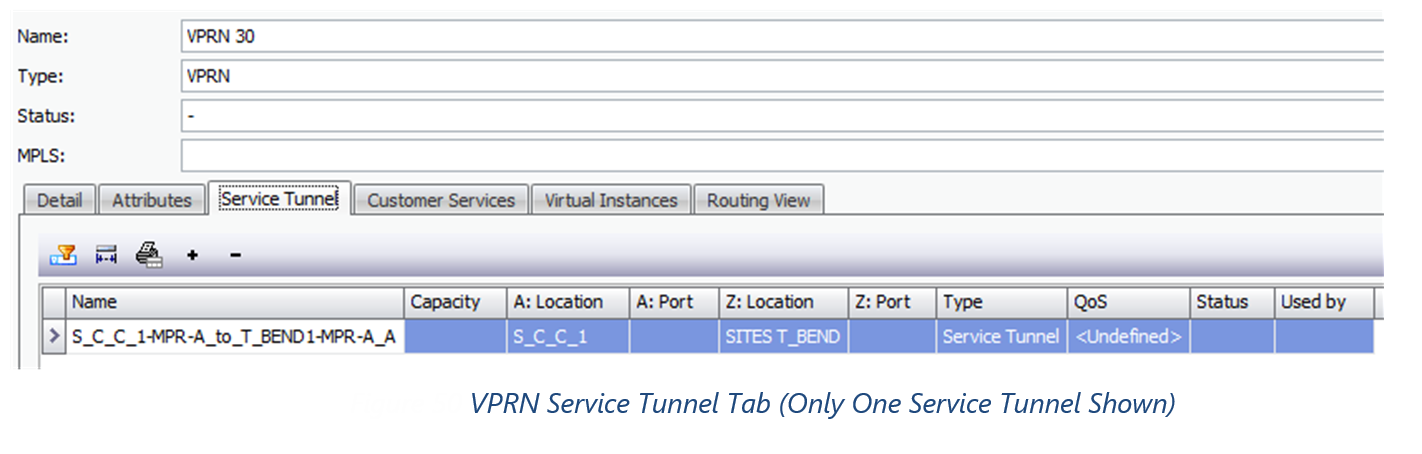
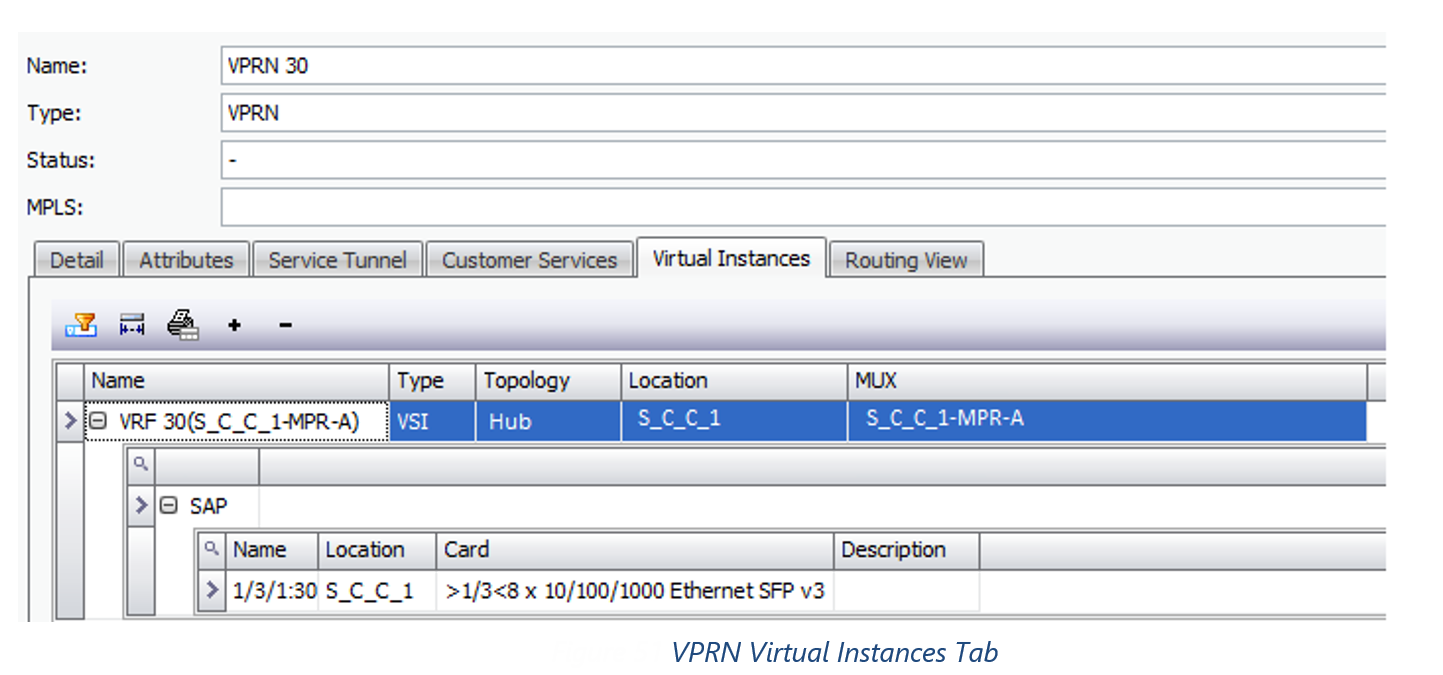
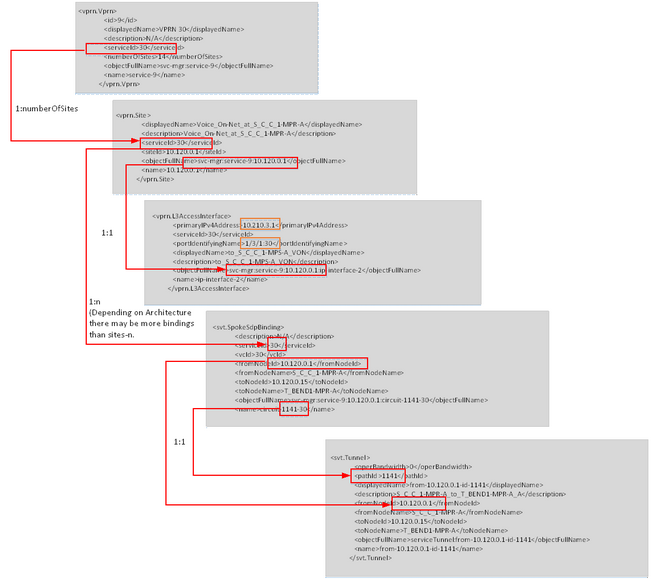
Field Mappings:
Source File – vprn.Vprn.xml (Initial Data Source for VPRN)
Source File – vprn.Site.xml (List of Sites associated with SAM VPRN Element)
Source File – vprn.L3AccessInterface (Provides associated SAP)
Source File – svt.SpokeSdpBinding.xml (Service Tunnel Binding Point to VPRN)
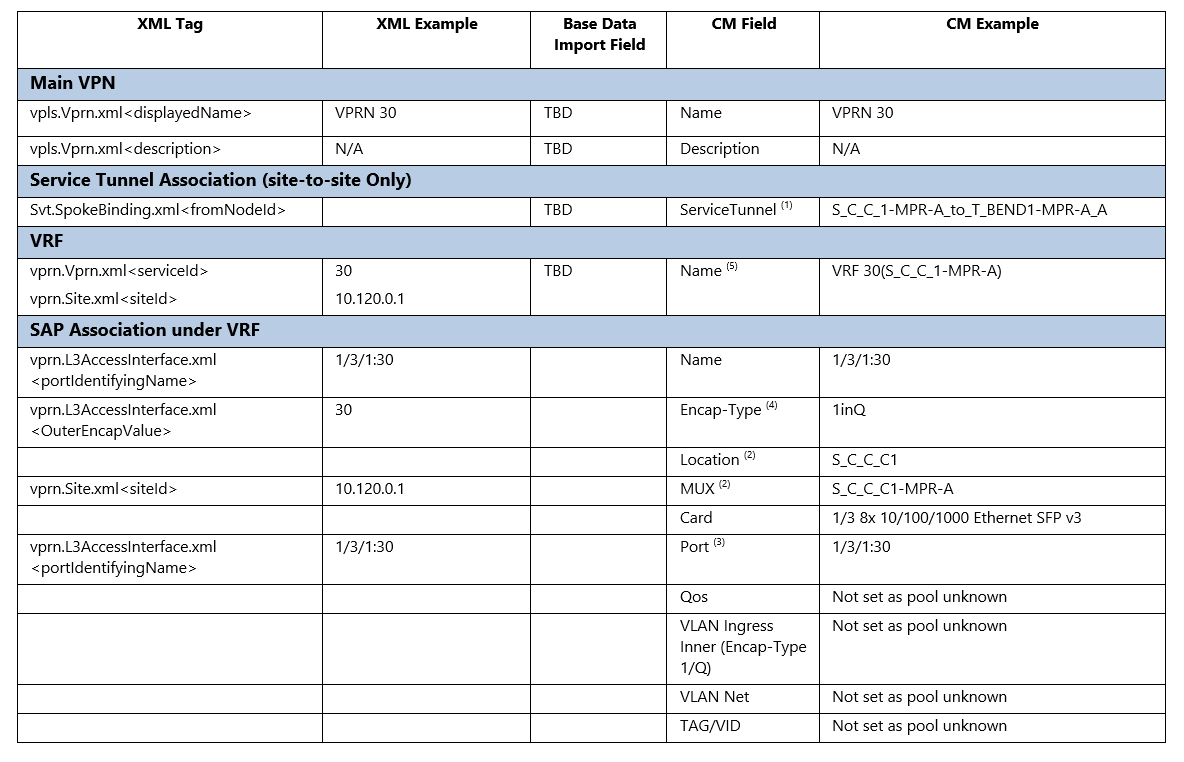
NOTES:
1)Local VPRN don’t have any Service Tunnel
2)Need to resolve Mux from <siteId> IP Address
3)Need to resolve Card/Port from <portIdentifyingName>, Ports can be Physical or Virtual Sub-Ports
4)If <OuterEncapValue> = 0 then Encap-Type = Null, otherwise = 1inQ
VRF Name will be created as VRF & ServiceId & (Site ID). Need to resolve SiteName from Site IP Address
XML VPRN Hierarchy